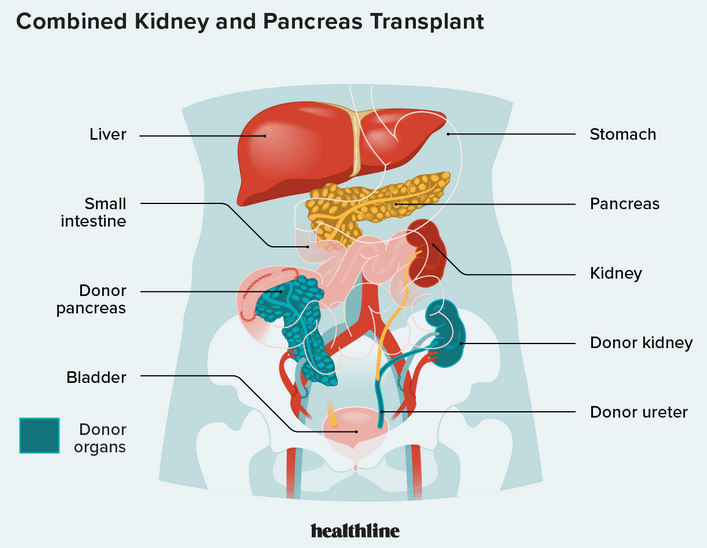
Kidney and pancreas transplantation are surgical procedures performed to replace a person’s damaged or non-functioning kidney and pancreas with healthy organs from a donor. These transplants are typically recommended for individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and diabetes mellitus, respectively, when other treatment options have been exhausted and their quality of life is severely affected.
Kidney Transplantation:
Kidney transplantation involves removing a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor and implanting it into a recipient whose own kidneys are failing. The goal is to restore kidney function, including the filtration of waste products and excess fluid from the body. The healthy kidney will typically be placed in the lower abdomen and connected to the recipient’s blood vessels and bladder. Kidney transplantation can significantly improve a person’s quality of life and overall health compared to dialysis.
Pancreas Transplantation:
Pancreas transplantation is typically done for individuals with type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas is not producing insulin, or for those with severe complications of type 2 diabetes. The procedure involves removing a healthy pancreas from a deceased donor and transplanting it into the recipient. A pancreas transplant can restore the ability to produce insulin, effectively managing blood sugar levels and reducing the need for insulin injections.
“Simultaneous Kidney and Pancreas Transplant (SKP) for Dual Severe Conditions”
In some cases, a simultaneous kidney and pancreas transplant (SKP) may be performed, particularly for individuals with both severe kidney disease (often due to diabetes) and diabetes-related complications. This procedure involves transplanting a healthy kidney and pancreas from the same donor into the recipient.
“Critical Factors and Ongoing Care in Transplant Procedures”
Transplantation procedures require careful matching of the donor and recipient, as well as lifelong immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted organs. The success of a transplant depends on factors such as the overall health of the recipient, the compatibility of the donor, and adherence to post-transplant care and medications. Regular follow-up and medical care are essential to monitor the function of the transplanted organs and manage any potential complications.
kidney-pancreas transplant life expectancy:
I can provide general information about kidney-pancreas transplants, but specific life expectancy, hospital recommendations, recovery time, success rates, waiting lists, and costs may vary based on individual circumstances, the healthcare system, and advancements in medical care. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals and specialized transplant centers for the most up-to-date and personalized information.
Life Expectancy after Kidney-Pancreas Transplant:
The life expectancy after a kidney-pancreas transplant can vary depending on various factors, including the recipient’s overall health, the success of the transplant, adherence to post-transplant care, and any potential complications.
Best Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Hospitals:
The “best” transplant hospitals may vary based on location, expertise, outcomes, and resources. Renowned medical centers with expertise in organ transplantation often have specialized transplant programs. Some well-known transplant centers in the United States include Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, Johns Hopkins Hospital, and Massachusetts General Hospital, among others.
Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Recovery Time:
The recovery time after a kidney-pancreas transplant varies for each individual, but it generally involves a hospital stay of about 1 to 2 weeks. Full recovery and stabilization of kidney and pancreas function may take several months, and ongoing monitoring and care are necessary.
Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Success Rate:
Transplant centers typically monitor and report the one-year and long-term success rates of kidney-pancreas transplants, which are influenced by several factors. These factors include the recipient’s overall health, donor compatibility, surgical skill, adherence to medication and follow-up care, as well as efforts to prevent complications.
Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Waiting List:
Patients in need of a kidney-pancreas transplant are placed on a waiting list maintained by transplant centers. Allocation of organs is based on medical urgency, tissue match, blood type, and waiting time. The waiting time for a kidney-pancreas transplant can vary based on factors like location, organ availability, and the individual’s specific circumstances.
Simultaneous Kidney-Pancreas Transplant:
A simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplant involves transplanting a healthy kidney and pancreas from a deceased donor into a recipient during the same surgical procedure. This procedure is typically done for individuals with diabetes-related kidney disease and diabetes itself.
Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Cost:
The cost of a kidney-pancreas transplant can vary depending on the country, healthcare system, insurance coverage, and individual circumstances. It often includes pre-transplant evaluation, the transplant surgery itself, hospital stay, immunosuppressive medications, post-transplant care, and follow-up appointments.
Kidney-Pancreas Transplant Steps:
The general steps involved in a kidney-pancreas transplant include: a. Pre-transplant evaluation and assessment of the recipient’s suitability for the transplant. b. Placement on the waiting list and donor matching. c. Surgical procedure to remove the donor kidney and pancreas, and the transplantation into the recipient. d. Post-transplant care, including monitoring for organ function, immunosuppressive medications, and recovery.
Success Rate of Kidney and Pancreas Transplant:
Success rates vary based on factors such as the recipient’s overall health, compatibility with the donor, surgical expertise, and post-transplant care. Generally, kidney and pancreas transplants have good success rates with a significant improvement in quality of life and organ function.
Simultaneous Kidney and Pancreas Transplants (SKP):
Simultaneous kidney and pancreas transplants are done for individuals with type 1 diabetes and kidney failure. This approach addresses both conditions in one surgery, enhancing quality of life and improving blood sugar control through the new pancreas while also addressing kidney function.
Longevity of Kidney and Pancreas Transplants:
The longevity of kidney and pancreas transplants varies from person to person. With proper care, immunosuppressive medications, and regular medical follow-ups, transplanted kidneys and pancreases can last for many years, often providing improved quality of life and alleviating complications associated with kidney failure or diabetes.
Complications of Kidney and Pancreas Transplants:
Short-term complications can include infection, bleeding, organ rejection, side effects of medications, and surgical complications.
Long-term complications may involve chronic rejection, infections, high blood pressure, diabetes (in kidney recipients), metabolic issues (in pancreas recipients), and potential side effects of immunosuppressive medications.
Informed Decision-Making:
It’s essential to consult with transplant specialists and healthcare professionals for the most up-to-date and personalized information regarding success rates, potential complications, and the overall management of kidney and pancreas transplantation. Advances in medical science and transplantation techniques may have occurred since my last update, impacting success rates and management approaches.
Causes:
Kidney and pancreas transplantation are treatments for specific medical conditions rather than conditions themselves. I’ll provide information about the common medical conditions that lead to the need for kidney and pancreas transplants:
Kidney Transplantation Causes:
The most common cause of needing a kidney transplant is end-stage renal disease (ESRD). ESRD occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to function effectively and filter waste products and excess fluid from the blood. The primary causes of ESRD include:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetes
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units)
Polycystic kidney disease (a genetic disorder causing cysts in the kidneys)
Pancreas Transplantation Causes:
Pancreas transplantation is primarily done to treat severe cases of diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, and sometimes type 2 diabetes with severe complications. The main causes include:
- Type 1 diabetes: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Complications of type 2 diabetes: Severe cases where diabetes-related complications significantly impact the individual’s quality of life, such as kidney failure and problematic blood sugar management.
Both kidney and pancreas transplantation aim to improve the recipient’s overall health and quality of life by addressing the underlying causes and restoring organ function.
“Transplantation: A Last Resort After Exhausting Other Treatment Options”
It’s important to note that healthcare professionals typically consider transplantation after other treatments, such as medications, lifestyle changes, and dialysis (for kidney disease), have been exhausted or are no longer effective in managing the respective conditions. The healthcare team makes the decision for an individual to undergo a kidney or pancreas transplant based on a thorough evaluation of their medical history, current health status, and suitability for the procedure.
Effect Kidney and pancreas transplantation:
Kidney and pancreas transplantation can have profound effects on a person’s health and overall quality of life, particularly for those suffering from end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or severe diabetes. Here are the primary effects of kidney and pancreas transplantation:
Improved Organ Function:
Transplantation replaces a failed or non-functioning kidney and pancreas with healthy organs, restoring their essential functions. A functioning kidney helps filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood, while a functional pancreas produces insulin, regulating blood sugar levels.
Enhanced Quality of Life:
Transplant recipients often experience a significant improvement in their quality of life. They are no longer reliant on dialysis or frequent insulin injections, which can be time-consuming and restrictive.
Normalization of Blood Sugar Levels:
In pancreas transplantation, the transplanted pancreas can often restore the body’s ability to produce insulin, effectively managing blood sugar levels. This can reduce or eliminate the need for insulin therapy and improve diabetes control.
Reduced Complications:
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, pancreas transplantation can help prevent or reduce diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and kidney disease. Similarly, kidney transplantation helps reduce complications associated with kidney failure and dialysis.
Enhanced Longevity and Survival Rates:
Kidney and pancreas transplantation can extend the life expectancy and improve the survival rates of recipients compared to those remaining on dialysis or managing diabetes with medications alone.
Decreased Healthcare Costs:
The initial cost of transplantation and ongoing immunosuppressive medications may be high; however, over the long term, transplantation can prove to be cost-effective compared to long-term dialysis or other continuous diabetes management strategies.
Restored Normal Daily Activities:
Transplantation allows recipients to engage in a more normal and active lifestyle without the constraints of dialysis schedules, dietary restrictions, or insulin management regimens.
Immunosuppressive Medications Requirement:
Transplant recipients need to take immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection. These medications suppress the immune system, and while they are crucial for transplant success, they may have side effects and require lifelong monitoring.
Potential Complications and Risks:
Like any surgical procedure, kidney and pancreas transplantation carry inherent risks, including infection, bleeding, organ rejection, and complications associated with immunosuppressive medications.
Synopsis Kidney and pancreas transplantation:
Creating a synopsis for kidney and pancreas transplantation involves summarizing the key aspects of these procedures, including their purpose, the surgical process, recovery, and potential outcomes. Here’sa concise synopsis:
Synopsis:
Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation Kidney and pancreas transplantation are life-saving surgical procedures aimed at replacing damaged or non-functioning organs.
Purpose:
Kidney Transplantation: Addresses end-stage renal disease (ESRD) by replacing failed kidneys, restoring filtration and waste removal functions.
Pancreas Transplantation: Treats severe diabetes (often type 1), replacing the pancreas to regulate blood sugar levels and mitigate diabetes-related complications.
Procedure:
Kidney Transplantation: Involves removing a healthy kidney from a donor and surgically implanting it into the recipient’s lower abdomen, connecting blood vessels and bladder.
Pancreas Transplantation: Usually a simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplant, replacing both organs from a deceased donor in one surgical procedure.
Recovery:
Post-surgery, patients undergo a recovery period, including monitoring organ function, managing medications, and healing from the surgery.
Rehabilitation involves regaining strength, adjusting to immunosuppressive drugs, and learning to manage blood sugar levels (for pancreas recipients).
Outcomes:
Transplantation leads to improved quality of life, normalized organ function, and enhanced longevity.
For pancreas recipients, it often results in stabilized blood sugar levels and reduced diabetes-related complications.
Considerations:
Lifelong immunosuppressive medications are necessary to prevent organ rejection and manage potential side effects.
The success of the transplant depends on careful donor-recipient matching, adherence to post-transplant care, and overall health.
Transplant Success Rate:
- Kidney Transplant Success Rate:
One-year survival rates for kidney transplants are generally very high, often exceeding 90-95%.
Long-term survival rates (5 years or more) are also favorable, with survival rates typically exceeding 80-85%.
- Pancreas Transplant Success Rate:
One-year survival rates for pancreas transplants are also quite high, often exceeding 90%.
Long-term survival rates for pancreas transplants are generally good, with survival rates varying based on the specific type of transplant (e.g., simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplant).
-
Simultaneous Kidney-Pancreas Transplant (SKP) Success Rate:
SKP, which combines a kidney and pancreas transplant in one surgery, generally has favorable success rates, providing both improved kidney function and better blood sugar control for individuals with type 1 diabetes and kidney failure.
Sympotus Kidney and pancreas transplantation:
It seems you are seeking information regarding the symptoms or indications that may necessitate a kidney or pancreas transplant. However, it’s important to clarify that kidney and pancreas transplantation do not treat specific symptoms; instead, they are surgical procedures aimed at addressing severe medical conditions. I will provide information about the conditions that may lead to the need for kidney and pancreas transplants:
Conditions Indicating the Need for Kidney Transplantation:
- End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): Advanced stage of chronic kidney disease where the kidneys no longer function effectively, leading to a buildup of waste products and fluids in the body.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Progressive loss of kidney function over a period of time, which can eventually result in ESRD.
Conditions Indicating the Need for Pancreas Transplantation:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, often leading to dependence on insulin injections for blood sugar management.
- Severe Type 2 Diabetes with Complications: In some cases, individuals with severe type 2 diabetes and significant complications may be considered for a pancreas transplant.
“Careful Evaluation and Decision-Making for Kidney or Pancreas Transplantation”
It’s important to note that a healthcare team, including specialists in transplantation, must thoroughly evaluate and assess an individual to determine the suitability and necessity of a kidney or pancreas transplant. The decision to proceed with a transplant is based on various factors, including the severity of the condition, overall health, and the exhaustion or inadequacy of other treatment options.
Conclusion Kidney and pancreas transplantation:
In conclusion, Kidney and pancreas transplantation are vital surgical procedures that medical professionals perform to address severe medical conditions and significantly enhance the lives of individuals suffering from end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or severe diabetes. These transplants aim to restore essential organ functions, improve the quality of life, and potentially extend lifespan.
In summary, individuals have a chance for a healthier, more active life through kidney and pancreas transplantation. It which address severe medical conditions and restore vital organ functions. The individual carefully evaluates and personalizes the decision to undergo a transplant, considering their unique medical history and circumstances. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and transplant specialists is essential to make informed decisions and achieve the best possible outcomes.
Faqs:
-
How long do kidney and pancreas transplants last?
The longevity of transplants varies for each individual, but with proper care and medication, transplanted kidneys and pancreases can last for many years, often providing an improved quality of life.
-
What are the potential complications of kidney and pancreas transplants?
Complications can include infection, bleeding, organ rejection, side effects of medications, surgical complications, chronic rejection, high blood pressure, infections, and metabolic issues, among others.
-
What is the recovery like after a kidney and pancreas transplant?
Recovery involves a period of post-surgery monitoring, medication management, rehabilitation, and adapting to immunosuppressive drugs. The timeline varies, but recipients can resume normal activities with time.
-
How are donors for kidney and pancreas transplants selected?
Donors are carefully evaluated based on medical, genetic, and compatibility criteria to ensure a successful transplant and minimize the risk of complications
Read more: https://ysblogger.com/category/all-about-health/
YSBlogger.com offers an insightful and comprehensive array of health-related content. Whether you’re interested in tips for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, in-depth discussions on various medical conditions, or the latest trends in fitness and nutrition, YSBlogger.com provides well-researched and expertly written articles.