Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but with increased awareness and advancements in medical technology, early detection can save lives. Knowing the signs, symptoms, and methods of early detection is crucial in battling this disease and empowering individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey. This article aims to offer a clear understanding of breast cancer, its warning signs, and how early detection can make a difference.
What Is Breast Cancer?
When aberrant cells in the breast grow out of control and form a tumour, breast cancer starts. These cancerous cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. While breast cancer is more common in women, men can also develop it, though at much lower rates.
There are several types of breast cancer, the most common being ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Other types, like invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), are less common but equally significant. Each type of breast cancer behaves differently, which affects treatment and prognosis.
Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
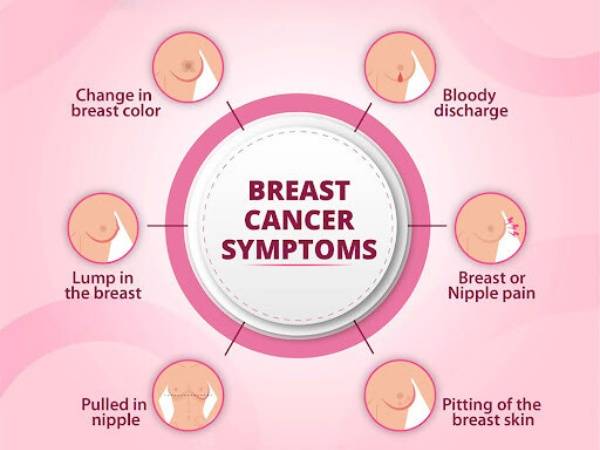
Understanding the signs and symptoms of breast cancer is critical to detecting it early. While some symptoms are visible or palpable, others may only be found through medical tests. The following are the main symptoms and indicators to look out for:
- Lump in the breast or underarm: One of the most common symptoms of breast cancer is a lump or mass in the breast or armpit area. While not all lumps are cancerous, it’s essential to have any unusual growths examined by a healthcare professional.
- Changes in breast shape or size: Noticeable changes in the size, shape, or contour of the breast, especially if they occur without any clear cause, may be a warning sign of breast cancer.
- Nipple discharge: Any unusual discharge from the nipple, particularly if it is clear or bloody, should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Nipple inversion: If the nipple turns inward or changes position, this could be a symptom of breast cancer.
- Skin changes: Redness, scaling, or thickening of the skin on the breast or nipple can indicate a more aggressive form of breast cancer. A dimpled appearance resembling an orange peel, known as peau d’orange, can also be a sign.
- Persistent pain: While not as common, unexplained or persistent pain in the breast or chest area could signal breast cancer.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing breast cancer. These include:
- Age: As people age, especially after the age of fifty, their risk of developing breast cancer rises.
- Family history: Women with close relatives (mother, sister, or daughter) who have had breast cancer are at higher risk.
- Genetic mutations: Mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 increase the likelihood of breast cancer.
- Hormonal factors: Long-term hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and early menstruation or late menopause can raise the risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity are linked to a higher risk of breast cancer.
Importance Of Early Detection
Early detection of breast cancer significantly improves survival rates and treatment options. When diagnosed at an early stage, breast cancer is more likely to respond effectively to treatment, and the chances of a full recovery are higher. The following screening methods can aid in early detection:
- Self-breast exams: Women should regularly perform self-breast exams to detect any changes in their breasts. While this is not a substitute for professional screenings, it is a proactive measure in noticing abnormalities early.
- Mammograms: A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast that can detect cancerous tumors before they can be felt. Women aged 40 and above are generally recommended to have yearly mammograms, but those with higher risks may start earlier.
- Ultrasound and MRI: These imaging techniques can be used alongside mammograms, especially for women with dense breast tissue or those at higher risk.
- Genetic testing: For those with a family history of breast cancer, genetic testing for BRCA mutations can help assess risk levels and determine preventive measures.
Breast cancer remains a serious health concern, but early detection offers hope. By understanding the signs, symptoms, and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps in maintaining their health. Regular screenings, self-exams, and awareness of bodily changes are critical tools in the fight against breast cancer. The earlier it is detected, the better the chance of a successful outcome, making vigilance an essential aspect of breast cancer prevention and care.